Digital commerce is still expanding extremely rapidly in the US, and both normal e-commerce and quick commerce (q commerce) seem to have future success. The Q-commerce industry is predicted to generate $195.01 billion in 2026. This is so because more individuals want on-demand and quick delivery of services. From 2026 to 2030, the market is expected to rise at a CAGR of 7.74% and be valued at US$283.04 billion by that year.
Standard e-commerce sites remain leaders as the eCommerce business is estimated to generate $4.32 trillion in 2026. Should the market expand at an 8.02% annual pace from 2026 to 2029, it would reach US$5.89 trillion by 2029. These figures highlight the size and value of both models as they continue to reshape consumer expectations and determine the course of online shopping going forward.
Looking at a top q commerce app- Instacart, this tendency is really evident. In the past quarter, 77.5 million sales raised the GTV to $33.4 billion in 2024, i.e. 10.2% more than the previous year. These figures indicate that fast-paced service is being desired by more individuals and that quick commerce is growing in significance in the broader eCommerce scene. To better understand how these two business models stack up and what distinguishes them, let’s examine more carefully the primary advantages and disadvantages of quick commerce vs eCommerce.
What is Quick Commerce?
Quick commerce is a fast-expanding internet shopping method. Usually within 10 to 30 minutes, delivering food, medications, and other daily needs in less than an hour is what it excels at. This rapid delivery strategy satisfies the increased need for speed and simplicity, thereby influencing behavior and expectations among individuals.
Using hyperlocal fulfillment facilities, dark stores, and optimal delivery routes, Quick Commerce is unique from other e-commerce systems. Through smartphone apps and other digital commerce platforms, they allow businesses to provide ultra fast delivery. Cities that have a high demand for products delivered exactly when needed are particularly interested in this method.
Speed-Driven Delivery Model
Quick Commerce is famous for its lightning-fast service, completing most orders in less than thirty minutes. This strategy gives consumers instant gratification and reduces delivery times by using local facilities.
- 10–30 minute deliveries
- Focus on urgent and impulse buys
- Ideal for metropolitan and dense urban areas
- Reinforces customer satisfaction
Hyperlocal Fulfillment Infrastructure
Quick commerce enterprises take advantage of dark stores and fulfillment facilities loaded with dairy products. These centers are positioned near clients to provide fast service.
- Small-scale warehouses within city limits
- Stock fast-moving, high-demand products
- Efficient last-mile delivery solutions
- Reduces shipping distances and times
Technology and Automation
From supply management to system setup, this model makes use of several machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data-driven concepts to enable more seamless operation.
- Automated inventory management
- Real-time order tracking
- AI-based delivery route optimization
- Predictive analytics for better demand planning
Start Selling Online Today – Get Your Custom eCommerce Store Built Now!
What is eCommerce?
Electronic commerce, often known as “e-commerce,” is the buying and selling of goods and services online. It adds business models like C2C (consumer-to-consumer), B2C (business-to-consumer), and B2B (business-to-business). From anywhere, online customers may review items, check pricing, and make purchases at any moment. One only needs a few clicks or touches.
This kind of internet buying has fundamentally transformed consumer behavior as well as global commerce dynamics. At the same time, q commerce concentrates on quick delivery, while traditional e-commerce stresses a greater selection of items, secure transactions, and a larger reach. From little neighborhood businesses to massive retail centers, it operates everything from simple, local companies to saving money, providing more alternatives, and simplifying processes.
Types of eCommerce
Although e-commerce operates in many ways, each one satisfies the needs of a distinct market. These include B2C, B2B, C2C, and even D2C (direct-to-consumer), which allows individuals to interact and do business online in a number of ways. eCommerce development service providers help you build a high-performing website.
- B2C: Amazon, Walmart
- B2B: Alibaba, ThomasNet
- C2C: eBay, Facebook Marketplace
- D2C: Brand-owned Shopify stores
Key Features of eCommerce
Modern e-commerce sites simplify shopping by using innovative procedures and technologies. Features like artificial intelligence-powered search and recommendation algorithms pique customer interest.
- 24/7 shopping access
- Diverse product catalogs
- Secure payment gateways
- Personalized shopping experiences
Advantages of Traditional eCommerce
Although traditional eCommerce lags behind q-commerce, it offers a number of excellent advantages like reduced prices, global access, and growth capability.
- No physical store requirement
- Easier business expansion
- Lower operational overhead
- Data-driven marketing
Benefits of the Quick Commerce Model
By satisfying customer requirements for fast delivery, simplicity of use, and immediate delight, the q commerce business strategy is altering online shopping behavior. Unlike most internet buying, q commerce is mostly about getting daily items right for individuals. Growing consumer expectations drive rapid trade, which offers five primary advantages backed by real-world business sector examples.
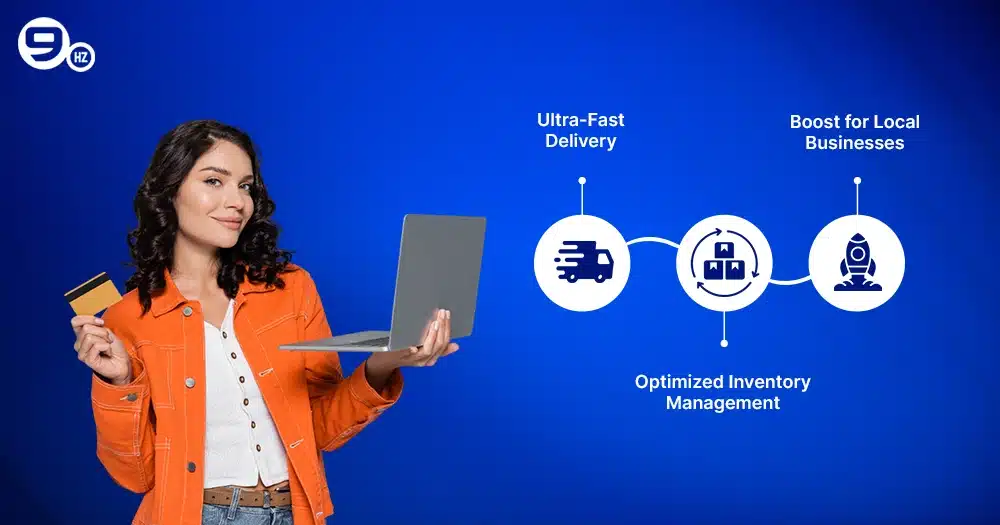
1. Ultra-Fast Delivery
One of q-commerce’s greatest features is its ability to transport goods extremely rapidly—often in only thirty minutes. For instance, Gopuff in the US advertises rapid delivery of everyday needs, household goods, and snacks via micro-fulfillment stores positioned in strategic locations. This service perfectly aligns with the hectic lives of urban residents.
2. Optimized Inventory Management
To simplify product administration, quick shopping systems also use real-time data and AI. DoorDash DashMart is one outstanding example, as it leverages hyperlocal demand analytics to ensure micro-warehouses have the correct inventory level. This feature allows consumers to constantly have minimal wait times for the things they want.
3. Boost for Local Businesses
Furthermore, local small businesses benefit from q commerce services quite a lot. For instance, Instacart helps small food stores all throughout the United States access more customers by means of on-demand delivery. Cooperation makes things more obvious and promotes the local economy.
Benefits of the eCommerce Model
The e-commerce model remains robust due to its ability to adapt, expand, and cater to a wide range of users. Quick Commerce aims for speedy delivery, while regular e-commerce sites offer a methodical approach to growth. If companies have the correct tech stack, they can effectively service local and worldwide markets. This capability allows companies to meet the demands of growing consumer bases and drive trends in online shopping.
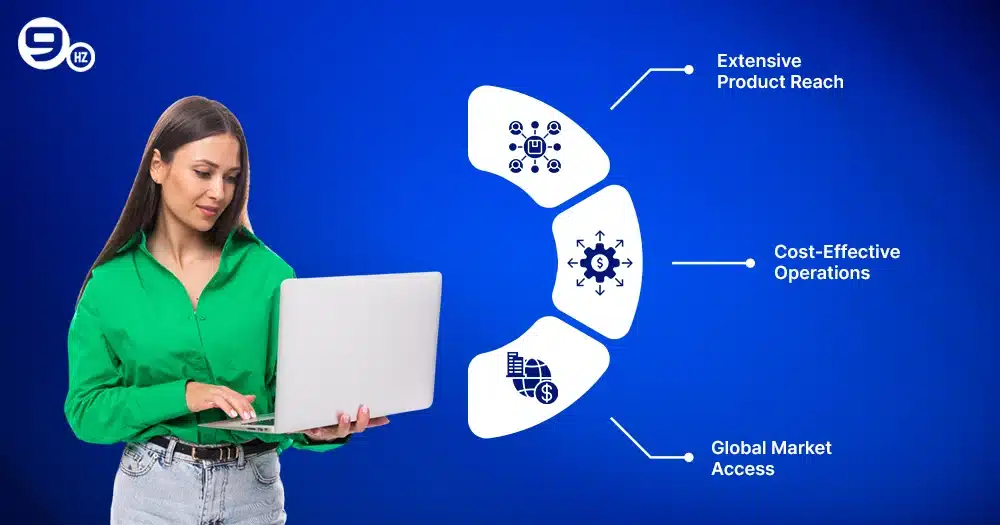
1. Extensive Product Reach
The fact that e-commerce sites may carry a wide variety of items is among their finest features. While traditional commerce only sells daily items, e-commerce offers everything from furnishings to devices. For instance, Amazon’s marketplace concept enables millions of products from many vendors to dwell together in one digital environment.
2. Cost-Effective Operations
E-commerce businesses employ centralized storage and improved transportation, which helps to explain their typically reduced additional expenses. For instance, Shopify vendors may build storefronts without using real locations, therefore cutting expenses like electricity, personnel, and rent. This is not the case with the q commerce business model, which requires a lot of money to establish transportation networks and has significant operational expenses.
3. Global Market Access
While q commerce procedures only apply in certain regions, e-commerce transcends national boundaries. Small companies have no trouble selling products all across the globe thanks to eBay and Alibaba. These platforms link vendors and buyers worldwide by reaching more people and enabling growth in ways that traditional commerce businesses cannot. Online buying is ideal for gradually developing a brand, as the process allows for flexibility.
Turn Visitors into Buyers – Build Your Conversion-Optimized Store Today!
Quick Commerce vs eCommerce
Digital retail currently consists of two forms: regular e-commerce and q commerce. Although e-commerce and quick commerce platforms serve distinct types of consumers and operate differently, both appeal to Internet buyers. While e-commerce offers a lot of things and may reach many people, q commerce is all about providing fundamentals to individuals extremely rapidly. These are some of the primary differences between them.
| Features | eCommerce | Quick Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | 1–5 days | 10–30 minutes |
| Product Range | Broad – includes electronics, apparel, and more | Limited – focuses on everyday essentials |
| Operational Cost | Lower due to centralized warehouses | High due to fulfillment centers and fast logistics |
| Geographic Reach | Regional to global | Local and hyper-local only |
| Consumer Behavior | Planned purchases | Impulsive, on-demand buying |
| Delivery Infrastructure | Warehouses, 3PL partnerships | Dark stores, micro hubs, and in-house fleets |
| Use Cases | Furniture, fashion, gadgets | Food delivery services, OTC meds, and groceries |
| Technology Use | CRM, AI for recommendations | Machine learning for route optimization |
| Sustainability | Easier to implement sustainable practices | Challenging due to fast delivery demands |
| Customer Satisfaction | High when delivery is timely | High due to instant delivery |
The table above clearly shows the fundamental distinctions between e-commerce and rapid trade. Among these variations are delivery time, product range, infrastructure, and environmental friendliness. Regarding scope and worldwide reach, e-commerce systems are the finest. On speedy delivery and quick gratification, however, Q-commerce businesses are the best. Understanding these variations enables businesses and consumers to choose the strategy that satisfies their demands as well as those of changing client demands.
Pro Tip: Reach more people with e-commerce; move swiftly with quick commerce. This combination of strategies makes customers happy and satisfies a great spectrum of their wants.
Don’t Just Sell, Dominate Online – Launch Your eCommerce Website Today!
Challenges of the Quick Commerce Model
Though it needs to cope with major issues, the q commerce business model is revolutionizing online buying with lightning-fast delivery. Due to rising operational expenses and ineffective service, q commerce companies must continually adapt to meet evolving consumer requirements without compromising their ability to turn a profit or remain viable.
1. High Operational Costs
Running a q commerce platform requires a lot of money to be invested in hidden stores, distribution hubs, and transportation staff in order for rapid delivery service. Maintaining this type of technology in real time results in set expenses. For instance, US-based quick-commerce company GoPuff has heavily invested in micro-fulfillment centers across many locations to ensure lightning fast delivery, yet running these centers entails great expenses.
2. Inventory Management Pressure
Delivering daily items to individuals in minutes necessitates accurate inventory control. Being late or lacking adequate supply could irritate consumers. Popular US food delivery company Instacart has struggled to maintain real-time inventories across many supermarket outlets. Many revisions or cancellations of orders resulting from these factors have slowed down delivery and deteriorated the entire experience.
3. Delivery Route Optimization
Optimizing delivery routes helps guarantee rapid delivery services. However, failing transportation initiatives and erratic city traffic make goods more costly and take more time to reach consumers. One large US last-mile delivery firm is DoorDash. Although they use advanced route planning techniques, they still struggle with traffic in cities and locating drivers, therefore compromising delivery services and wasting resources.
Challenges of the eCommerce Model
Despite its many issues, e-commerce has transformed the way consumers shop by offering more options and streamlining processes. From the expense of attracting fresh clients to the intricacy of the supply chain, e-commerce businesses have to constantly generate fresh ideas to remain expanding and profitable.
1. High Customer Acquisition Costs
To attract and retain online consumers, you must spend a lot of money on marketing, such as commercials, SEO, and discounts. Big US online furniture retailer Wayfair spends a lot on digital marketing to attract more consumers, but the expenses of acquiring new ones are rising, thereby compromising their profit margins. Many traditional retailers on internet struggle with this.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics Complexities
Big e-commerce companies have a lot of challenges, like ensuring timely delivery of items and fast filling of orders. Walmart’s online store needs to control massive stocks and intricate transportation networks if it is to compete with Amazon. Their difficulties with product availability and last-mile transportation slow down overall delivery services and satisfy fewer consumers.
3. Cart Abandonment and Conversion Rates
People quit their shopping carts online for various reasons, including security concerns, lengthy checkout times, and surprising pricing. The largest e-commerce platform available in the US, Shopify, constantly improves the checkout experience for vendors. Still, the organization is experiencing issues optimizing conversion, which compromises overall sales performance.
Industries Where Quick Commerce and eCommerce Play a Major Role
Quick Commerce and e-commerce have revolutionized consumer behavior by enabling quicker, simpler, and more diverse experiences in many spheres. While standard ecommerce sites allow you to purchase a number of different goods, including gadgets and digital services, q commerce is perfect for delivering daily items to you extremely quickly. Ecommerce and Q commerce taken together are altering consumer behaviour and supply chain management globally.
Quick Commerce
Food Delivery
Quick Commerce expedites the delivery of meals from local restaurants and cloud kitchens, thereby meeting people’s immediate food needs. By providing a large selection of fresh meals within minutes, particularly at lunch and dinner periods when consumer demand is strong, q commerce space serve individuals who live in busy cities by using real-time recording and simple-to-use mobile applications.
- High demand during peak meal times
- Freshness ensured by local kitchens
- Real-time order tracking improves experience
Over-the-Counter Medications
This company promptly provides over-the-counter medications like cold medications, allergy meds, and painkillers. Quick commerce firms ensure that customers may rapidly get these health products without leaving their houses. Furthermore, these q commerce sites closely follow inventory and regulatory guidelines to ensure deliveries are safe and on schedule and often offer digital health advice.
- Critical for urgent health needs
- Requires strict inventory compliance
- Often offers health information features
Grocery and Everyday Essentials
The main objectives of Q Commerce include fast and precise delivery of food and household goods. It’s great as people can acquire fresh food, cheese, and cooking tools straightaway. Good product management and specialized dark stores help quick commerce businesses satisfy everyday demands. Families and city dwellers who seek convenience particularly love these services.
- Freshness and stock accuracy vital
- Localized hubs improve delivery speed
- Popular among urban and busy consumers
eCommerce
Electronics
Online buying sites enable you to choose from a vast array of equipment, laptops, and cell phones. These websites also provide extensive product information, including consumer reviews. Consumers want secure methods of payment and assurance of options. The increasing number of people using technology means that traditional e-commerce must provide speedy tech support to keep consumers satisfied, build trust, and ensure seamless delivery of delicate goods.
- High-value purchases needing security
- Warranty and support included
- Detailed product info boosts confidence
Fashion & Apparel
With large collections, annual trends, and influencer marketing, fashion ecommerce performs really well. Customers like well-selected fashions, simple returns, and sizing recommendations. To attract more people to connect with and purchase from them, online platforms likewise heavily invest in graphic content and tailored recommendations. Such investment is done to attract consumers seeking quickness without compromising flair.
- Influencer marketing drives trends
- Visuals and size guides crucial
- Flexible returns enhance trust
What are the Main Differences?
Standard e-commerce and Q-commerce vary in ecommerce depending on speed versus range. Shipping timeframes, product availability, technological usage, and consumer expectations are the primary factors that differentiate standard ecommerce from q commerce. These variations highlight how differently each strategy shapes behavior and what the future of Q-commerce and the future of online shopping. Let us once again review the fundamental distinctions:
- 1. Speed: Regular e-commerce typically takes 1–5 days to transmit; Q commerce may accomplish it in 10–30 minutes. People’s expectations of instant gratification are shifting in line with this quick service.
- 2. Product Type: Traditional eCommerce platforms offer digital products, apparel, and technology, among other items. Conversely, Q commerce only offers household goods and over-the-counter medications, and not luxuries.
- 3. Tech Use: To choose the optimum paths, Q Commerce depends on AI, machine learning, and real-time monitoring. Mostly employed in traditional eCommerce for marketing and customized recommendations is AI.
- 4. Business Model: Quick commerce takes advantage of local hidden businesses and small distribution hubs near cities to guarantee quick delivery. In the past, online buying relied on central storage and third-party managed shipping.
- 5. Consumer Expectations: Q commerce alters the guidelines for same-day, ultra-fast delivery, emphasizing speed and simplicity of use. Traditional eCommerce prioritizes pricing, range, and comprehensive information.
- 7. Operational Costs: Since Q. Commerce uses its infrastructure seven days a week, twenty-four hours a day, it has substantial expenses. While long-distance operations are more challenging, traditional eCommerce boasts reduced fixed expenses.
- 8. Geographic Reach: Since quick commerce primarily serves extremely nearby locations, it emphasizes fast delivery. Conversely, ecommerce sites may assist individuals in regional, national, or even worldwide spheres.
Concluding Thoughts on Quick Commerce VS eCommerce
Ultimately, both eCommerce and fast business offer advantages, so the one you choose will depend on your objectives. While eCommerce offers more items and better pricing comparisons, fast delivery is fantastic for addressing urgent requirements and receiving stuff quickly. Knowing your target audience and your company’s strategy can help you decide what to do.
If you are pondering about making either of these investments, NineHertz can assist you. Being professionals in eCommerce app development and quick commerce solutions, they create sturdy, scalable, and simple-to-use systems. Furthermore, their staff ensures that your company keeps ahead in the modern, fast-paced industry. The NineHertz is the ideal partner if you want to bring your digital concept to life. They can create either lightning-fast quick commerce software or a bespoke eCommerce website.
FAQS
1. What is the difference between Quick Commerce and eCommerce?
While eCommerce is all about having a larger selection of items, being able to develop, and reaching more people, quick trade is all about providing things right away to consumers. Therefore, the key differences include the speed of arrival, the target audience, and the management strategies employed.
2. What types of products are sold via Quick Commerce vs eCommerce?
Usually, Q Commerce offers daily needs like meal services and over-the-counter medications. Conversely, eCommerce sites market anything from gadgets and apparel to digital services and furnishings.
3. Which is faster: Q Commerce or E-Commerce?
Obviously, quick commerce is speedier as it delivers goods extremely rapidly (within 10 to 30 minutes), while normal eCommerce takes one to five days to fulfill orders.
4. Is Quick Commerce available everywhere?
This is not the case at the moment. Due to its reliance on hyperlocal delivery hubs, Q commerce primarily operates in cities and is not easily accessible in rural or distant areas.
5. Which offers better product variety: Q Commerce or E-Commerce?
While q commerce concentrates on the basics that consumers seek, regular eCommerce offers a larger range of items across various sectors.
6. What kind of logistics do Quick Commerce and eCommerce use?
Fast delivery firms use “dark stores” and “micro-fulfillment centers,” and Q-commerce companies utilize them. Conversely, e-commerce reaches more individuals by means of central warehouses and outside services.
7. Which model is more sustainable?
While q commerce has a tougher time being eco-friendly because it delivers goods in tiny quantities so quickly, normal eCommerce is often better at adjusting to ecologically friendly methods.
8. Can a business offer both Q Commerce and E-Commerce?
Sure. By combining q commerce for speed with eCommerce for diversity, companies can really satisfy a broad spectrum of consumers and keep ahead of the competition.
Great Together!