In recent years, there has been a high demand for cloud-based services due to their flexibility, on-demand scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Following the model, companies are adopting SaaS platforms like Google Workspace, Salesforce, or Microsoft 365 to fit into the cloud infrastructure. Research indicates that by 2030, the SaaS market will reach $887.05 billion, growing at a 15% annual rate from 2025.
So, if we compare SaaS Vs traditional software, it shows a detailed comparison on the majority of points of difference. Also, the SaaS development company is exploring new customisation to improve the SaaS platform and derive benefits over traditional software. What’s a more ideal option? In the blog ahead, we will be discussing the core difference and the process to choose the best alternative offering more flexibility at minimum upfront costs.
Understanding SaaS and Traditional Software
Before navigating the core distinction between SaaS and traditional software, it is crucial to understand the basics of these software, its development approaches, and its advantages. This way, the business will take an informed decision to select the right software that aligns with budget constraints, long-term growth, and operational needs.
What is SaaS (Software as a Service)?
Software as a Service is a cloud infrastructure-based model where users can directly download software or applications and access them through web browsers rather than buying them locally. Also, a cloud service provider manages the backend infrastructure, maintenance, security, and updates. SaaS works under a multi-tenant architecture where a single software serves multiple user accounts while maintaining privacy and data security.
Some of the popular types of SaaS platforms are:
- Modern CRM SaaS tools store customer data and analyse it using automation and forecast for business requirements. (Zoho CRM, Hubspot, and Salesforce)
- ERP SaaS software combines tracking and accounting records to check for risk management, compliance, and functionality for projects. (SAP Business, Odoo, and NetSuite)
- Project management SaaS unified operation through sync documents, dashboards, tracking tasks updates, real-time notifications, and reporting. (Trello, Jira, and Asana)
- eCommerce stores integrate unified features for sales, inventory operations, financial tracking, and payment without any IT infrastructure investment. (WixeCommerce, Shopify, and BigCommerce)
Start SaaS Development Now
Talk to our Experts
Request A Free Quote
What is Traditional or On-Premise Software?
The traditional software, also known as on-premise software installed and runs the individual servers and computers. Mostly, businesses are looking for access control and customisation, preferring this traditional software. For instance, finance and healthcare choose on-premise software to comply with legacy systems and privacy regulations.
On-premise software is installed on physical servers within the organisation’s facilities to manage all the updates, maintenance, backups, and security. Businesses approach software development companies for building the software, while they take full ownership and control over the software functionalities.
Why does this Comparison matter for Modern Businesses?
For modern businesses, investing in software becomes a strategic decision to impact finances, operations, and workflow processes. So, choosing between SaaS and traditional software does not remain a technical decision; this comparison affects the cost efficiency, scalability, security, and innovation capacity for the business.
SaaS software provides more flexibility and fits the budget that making it ideal for growing businesses and startups. While traditional on-premise software offers better control and customisation ideal for businesses with regulatory needs.
Navigating through the core differences will help to find the solutions that align with operational demands, business growth, and budget constraints.
| Factor | SaaS | Traditional Software |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based; accessible anywhere | On-premise; limited to the internal network |
| Cost | Subscription; low upfront | High upfront; long-term cost |
| Maintenance | Vendor-managed; auto-updates | IT-managed; manual updates |
| Customisation | Limited by the vendor | Fully customisable |
| Security | Vendor-controlled; external data storage | Full internal control; better for compliance |
| Scalability | Fast, add users/features easily | Slower, requires hardware/licenses |
| Offline Use | Requires internet | Works offline reliably |
Core Differences Between SaaS and Traditional Software
Business models are becoming more specific to deliver the value to the customer, whether it’s Customer to Business (C2B), Business to Customer (B2C), or (B2B) Business to Business. So, as the model differs, beyond the fundamentals, there are major points of difference between SaaS and traditional software. Let’s understand them:
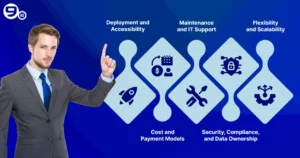
Deployment and Accessibility
Software as a Service is based on cloud infrastructure that can be accessed remotely through an internet connection. Businesses looking for flexible collaboration and operating across different departments can prefer this software so as not to be restricted to any specific location. Hence, this is more accessible software through multiple account logins.
Traditional software is confined to limited networks and connects with limited devices for security controls. It is deployed within the organisation’s infrastructure, and the software development company delivers for specific business purposes.
Cost and Payment Models
SaaS operates on a subscription model that follows an annual or a monthly basis. It requires no high upfront cost at once and helps businesses to scale faster. Following these pricing models, small-scale businesses and startups can easily access it through an interim payment and balance their finances.
Traditional software requires a high upfront cost to install within the organisation. It comprises major hidden costs for IT support, hardware costs, and maintenance fees. Opting for this software is a more economical alternative, supporting long-term usage and a stable user base.
Also Read
How Much Does It Cost to Build a SaaS Product?
Maintenance and IT Support
SaaS software providers are accountable for their maintenance, security patches, and upgrades. Businesses might require installing new versions with additional costs to extend their usability through new features. Vendors do provide 24-hour IT support to resolve queries and provide hassle-free maintenance.
Traditional software requires more time and money investment to update the software, depending on third-party vendors and hiring tech experts. It creates a dependence on the IT department for urgent bug fixes and regular updates.
Security, Compliance, and Data Ownership
SaaS providers are investing in cybersecurity and access control to secure cloud infrastructure. It offers security in multiple ways through multi-factor authentication, backups, and data encryption. However, as the data is stored on an external vendor’s servers, this might create risk and security vulnerabilities.
Traditional software acquires complete access control over data updates and in-house management. This makes traditional software more secure and fit for regulated industries that require compliance. However, it creates cost requirements that engage the IT department in security protocols to meet compliance needs.
Flexibility and Scalability
SaaS software allows for customisation, but with limitations based on the vendor’s terms. It provides moderate flexibility for a personalised experience to modify for roles, users, and workflow settings. Due to its versatile usage, SaaS platforms can be accessed through internet connections without any installations.
Traditional software offers more flexibility due to its complete ownership and ease of customisation for features. Businesses with specific requirements and technical expertise should opt for this software as it is built from scratch. Following custom software development, it provides regular updates and scalability.
Innovation and Feature Updates
SaaS platforms are consistently innovating through feature enhancements and faster deployment. It easily updates for security patches, integrates with automation tools, and AI-driven analytics to track for improved user experience without any downtime and additional efforts.
Traditional software takes longer for feature updates, depending on manual installations. Many times, this may be delayed due to department approvals and compatibility checks. Due to its complex architecture, this software resists adapting to changes and requires time to implement for required changes.
Advantages of SaaS (Backed by Real-World Use Cases)
Software as a Service (SaaS) operates through cloud-based infrastructure that does not require standard installation and offers remote cloud infrastructure to access through the web. It provides major benefits over traditional software, such as:
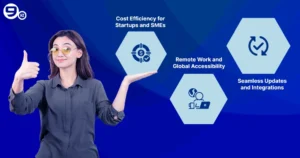
Cost Efficiency for Startups and SMEs
SaaS platforms are a cost-effective alternative as they work under a multi-tenant architecture. Generally, here the software license and hardware cost are comparatively lower, making it perfect for startups and SMEs. SaaS vendors also provide user base upgrades and scalability with flexible plans.
For example, Canva is a SaaS platform that empowers small businesses and agencies to develop high-quality designs and free mockups. It benefits them from expensive hirings and investing in paid tools for a high amount for minimal work.
Remote Work and Global Accessibility
A SaaS platform is a cloud-based infrastructure that offers flexibility to access from remote locations using the internet. It helps companies to work in a hybrid environment and connect to a global network as well, using a small account. It reduces the burden for the organisation to maintain different storage and backend systems, rather than a unified system for smoother operations with 24-hour support.
For instance, one of the world’s largest remote companies, GitLab, operates without any physical headquarters. Using SaaS platforms like Zoom, Slack, and other cloud-based tools to share a unified experience for the workforce.
Seamless Updates and Integrations
SaaS tools offer seamless and regular updates without interrupting their existing workflows. It extends its functionalities, modern SaaS platforms connect through APIs for flexible integration, and establish unified workflows within the infrastructure. SaaS providers are accountable for managing all maintenance and updates that reduce the burden of cost and resources.
We can understand that for the logistics industry, a SaaS platform like ShipStation is integrating different marketplaces as Shopify, Amazon, or eBay, and carriers for FedEx, for real-time tracking of packages and label printing.
Flexibility and Scalability
Businesses are not remaining a one-stop destination; this is expanding to multiple branches and aiming for global reach. SaaS platforms are designed to adapt to new trends with APIs and are scalable to reduce operational risks and ease implementation.
Let’s understand that by considering an eCommerce store made with Shopify, it can scale with offers at special occasions like Black Friday sales. SaaS platform handles multiple transactions and spikes demand for users at once without any downtime.
Business Connectivity
SaaS ensures seamless business connectivity with features of advanced firewalls, automation backups, multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, and disaster recovery measures. All these frameworks are provided by SaaS providers for cybersecurity and ensure businesses connect securely with users without any risk for data threats.
SaaS providers like Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure are offering built-in compliance protocols that adhere to industry standards. Even during the global crisis, AWS cloud-based SaaS was able to maintain its operations, supporting the majority of industries.
Advantages of Traditional Software (When Control is Critical)
From the access control perspective, traditional software is a more preferable option as it secures data within the organisation and eases customisation. Many industries, like healthcare and security, are backed by confidential research and development that requires more control measures. For a detailed understanding, here is the analysis of the advantages of traditional software:
Full Ownership and Customisation
One of the common advantages of traditional software is full ownership without any intervention from external vendors. Businesses can easily implement customisation to support their branding, operational processes, and unified workflows. Unlike SaaS platforms, it doesn’t limit customised features and can be modified to improve on the core architecture.
Better Fit for Specific Industry Regulations
It is ideal for businesses with strict regulations that require controlled data measures, regular process audits, and compliance protocols. Unlike SaaS, traditional software does not rely on a third-party vendor’s server for data management, but rather stores internally in a secure database system. Also, while hosting on-premises, it allows businesses to enforce compliance measures directly.
Reliability in Offline Environments
Traditional software can be accessed offline, which eliminates the risk of losing connectivity in remote areas. It doesn’t rely on cloud connectivity and can be managed through offline settings, beneficial for manufacturing and mining operations. It also saves costly downtime and business risk related to online networks.
Performance Optimisation
It is beneficial for industries facing issues related to data processing and speed latency. Traditional software can be optimised and run over specified hardware to support faster processing and high-performance compatibility. As the organisation has full ownership and control, this will be an ideal fit for applications and software with targeted purposes.
Long-Run Cost Stability
Traditional software requires high upfront costs during installation; however, the ongoing expense for maintenance is predictable. It ensures cost stability, unlike SaaS platforms, where vendors can put up any recurring fees and price escalations. Organisations are flexible in choosing to implement updates, adding features and planning for expenditure.
Choosing the Right Option: Practical Factors to Consider
Both the alternative SaaS and traditional software work for companies and benefit in their own ways. So, it is required to assess different practical factors to consider the right option that aligns with business requirements.
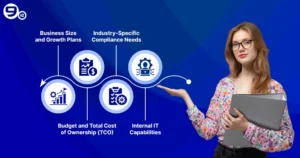
Business Size and Growth Plans
Based on the business size and growth plans play a major role in determining whether SaaS or traditional software is ideal. Generally, small-scale businesses and startups prefer SaaS due to its scalability and flexible terms. On the other hand, businesses with high scale and progressive growth plans might benefit from traditional software due to long-term control and deep customisation.
Budget and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Before deciding on SaaS or traditional software, you can analyse budget constraints and calculate the total cost of ownership. SaaS tools fit for a moderate budget with minimal license and subscription fees that is ideal for SMEs and startups. Traditional software requires a high upfront investment, but provides long-term benefits for updates and maintenance.
Industry-Specific Compliance Needs
If a business requires independent access control to comply with changing compliance needs, traditional software is an ideal fit to operate under strict security frameworks. Traditional on-premise software provides an organisation with comprehensive access control and compliance checks to secure sensitive data within its internal infrastructure. SaaS is exposed to risk of cyberattacks and data threats, and is dependent on the vendor’s control of access.
Internal IT Capabilities
Depending on the internal IT team’s expertise, the business can make a choice from the options. SaaS tools reduce the dependency on the IT team and ease access to download through web browsers using the internet. Traditional software requires a development team to build the software from scratch and an IT team to support easy installation, upgrades, customisation, and cybersecurity.
Vendors Lock-in and Flexibility
SaaS providers set up a lock-in period that restricts switching providers due to migration issues, integration dependencies, and contractual terms. On the other hand, traditional software provides long-term flexibility and makes it easier to customise for features, opting for vendors and an in-house integration system. Companies that rigidly follow one SaaS platform like Salesforce CRM might find it difficult to embed with data structure and custom workflows.
Data Migration
Next, the most overlooked factor is the flexibility for data migration, as business scaling for new products and verticals. Opting for the alternative that provides flexibility with APIs and data export capabilities without any delays. Also, following a hybrid approach will support critical operations and effectively manage data controls. Contract flexibility allows for easy migration through devices.
Expert Insights: SaaS vs Traditional Software in 2025
In 2025, SaaS tools will be the most preferred choice for businesses due to their flexible subscription-based model. Without high investment, companies prefer SaaS to avoid economic uncertainty and costly upgrades. Global tech is leading for dynamic innovations, and SaaS platforms provide an agile approach to build what businesses want in the fastest way possible.
Which Works Better for Small Businesses?
For small businesses like food delivery apps and other startups, SaaS tools would be a better alternative that does not require building an IT team. It also benefits from less investment, initially, with new ideas, businesses prefer not to risk high investment without measuring for return on investment.
Example: Small businesses are using SaaS based tools like Shopify and Zoho CRM to handle transactions and track deliveries, manage inventory, and store customer data without high investment into enterprise-level software.
Which Works Better for Large Enterprises?
Larger enterprises come with complex needs and requirements, looking for improved customisation, legacy systems, and handling global compliance. They need traditional software for their critical operational business; however, they use SaaS platforms for communication and information sharing services.
Example: Industries like insurance, banks, and security have complex transactions that need traditional software to operate on a larger scale with regulatory reporting. Although they can still use SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365 for effective collaboration and communication.
Hybrid Approaches – Combining SaaS with On-Premise
The ideal choice for the 2025 market trend is a hybrid approach to combine SaaS and on-premise for creating a balanced IT ecosystem. Businesses can drive more innovation, global accessibility, and collaboration using both choices. SaaS platforms will provide flexible plans and remote accessibility, while traditional software improves for customisation and support for offline reliability.
Start SaaS Development Now
Talk to our Experts
Request A Free Quote
Example: Global companies like Amazon and Google are building their SaaS platforms and traditional software to manage their user base, production controls, supply chain management, and enhanced collaboration across remote locations.
So, in 2025, when companies are aiming to innovate rapidly to face global competitiveness, the hybrid approach will exist to maximize operational efficiency, compliance measures, flexibility, and long-term competition. Key emerging trends for SaaS platforms include automation, vertical SaaS, low-code and no-code platforms, mobile-first SaaS, Web3 environment, and improved data privacy.
Conclusion: Making an Informed, Trustworthy Choice!
In the dynamic business world, it is essential to make a good comparison of SaaS and traditional software based on their features, advantages, and customization. As hybrid adoption is gaining momentum, businesses can handle operations across multi-cloud environments and push production through innovative approaches. Businesses should measure for overall comparison in terms of requirements, budget, and growth plans. Connecting with the best SaaS development company will ease the research on the benefits and services available.
FAQs on SaaS vs Traditional Software
Is SaaS more cost-effective than traditional software?
Yes, SaaS platforms are generally less expensive in comparison to traditional software and provide flexible plans for subscriptions.
Is SaaS as secure as on-premise solutions?
Yes, a SaaS development company provides advanced security through encryption protocols; however, through on-premise solutions, it creates the ultimate control and compliance.
Can large enterprises fully rely on SaaS?
It is advisable for larger enterprises not to rely on SaaS platforms only, as with the help of hybrid models, they get the benefits of accessibility, access control, and quick maintenance.
What are the hidden costs in both models?
Some of the key hidden costs in both models are that SaaS attracts high subscription fees in the long run, while on-premises carries additional costs for software upgrades, hardware, and hiring IT staff.
Great Together!