These days, more and more businesses are jumping on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) wave to stay ahead in a connected world. Well, from manufacturing and energy to logistics and healthcare, companies are starting to see how smart, connected systems can make work smoother, cut costs, and spark new ideas. It is not just another passing trend; it’s a real shift in how industries are taking steps forward.
According to Statista, the number of connected IoT devices worldwide is expected to cross 20 billion soon, and in the US alone, the IoT market could hit over $379.91 billion by 2025. With growth like that, businesses really need to think carefully about which IIoT platform they choose, one that can actually scale in the long run, keep data secure, and deliver real ROI.
Everything you need to know about choosing the top IIoT platform in 2025 is covered in this blog, including advantages, expenses, real-world case studies, and a final checklist to make the process easier. This guide will help you make a well-informed choice that aligns with your business objectives, whether you’re looking into IoT software development services or specialized IoT consulting services for deployment.
Understanding Industrial IoT Software
What is Industrial IoT Software and Why It Matters
Industrial IoT software is a digital platform that links machinery, sensors, and devices in an industry to gather and act upon data in real-time. IIoT is planned to take care of large-scale, mission-critical settings like supply chains and utilities, in contrast to consumer IoT applications like smart homes. Even a few hours of downtime can cost these companies a million dollars.
Why it’s important
-
Efficiency of operations: Constant observation guarantees smooth production and helps minimize machine downtime. This maximizes productivity, boosts throughput, and controls costs.
-
Predictive maintenance: Predictive maintenance can be identified using IIoT analytics, and events such as equipment failure can be identified before they even happen. Well, such can help in extending the lifespan of the machine, reducing the repair cost, and minimizing the unplanned breakdowns.
-
Data-driven choices: Real-time data only helps with performance bottlenecks and resource allocations. Decisions that are made by managers can be made even more quickly and accurately, besides increasing productivity and profitability.
-
Competitive advantage: Consumer demands can quickly be changed by using IIoT software. Quicker response time helps in increasing customer satisfaction and making the market positioning stronger.
IIoT software lays the foundation for innovation in the industry. It provides companies with a much more intelligent and healthy approach to their operations.
Also Read…
IoT App Development: How Much Does it Cost to Develop in 2022?
Key Components of Industrial IoT Solutions
Each IIoT platform is constructed on a number of fundamental layers that cooperate to provide value:
-
Device Layer: This comprises industrial machinery, sensors, and actuators that produce operational raw data. It makes it very easy to track conditions of the environment, health of the equipment, and real-time processes.
-
Connectivity Layer: Networks like LoRaWAN, Wi-Fi, and 5G help in the smooth transfer of data between devices and platforms. Dependable connectivity becomes essential when the industry wants continuous operations and real-time decisions.
-
Data Processing Layer: Data that is gathered is processed by cloud, edge, or hybrid computing systems. It makes it pretty easy for the business to optimize maintenance and make the production by converting raw inputs into insights.
-
Application Layer: Dashboards and visualization tools present the processed data in an understandable manner. Operators can make quick decisions thanks to these well-planned layers.
-
Layer of Security: Sensitive industrial data can be protected by features like compliance, encryption, and authentication. A healthy security framework helps in the prevention of cyberattacks.
Benefits of Industrial IoT for US Businesses
Industrial IoT software adoption by US businesses has several benefits:
-
Increased Productivity: With automated insights, you don’t have to waste time on boring reports or manual checks. Since the machines are always being watched, businesses can keep things running longer and make work way smoother.
-
Cost reduction: With predictive analytics, you can spot equipment problems before they actually break down. This way, businesses don’t have to deal with random shutdowns that cost a lot of money, and they can even cut maintenance costs by almost 40%.
-
Quality Control: Ongoing observation guarantees that goods fulfill constant quality requirements. IIoT software contributes to waste reduction, defect minimization, and increased customer satisfaction by identifying abnormalities early.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Strict US compliance requirements are easier to meet when data collection and reporting are automated. IIoT guarantees traceability and lowers the possibility of fines or legal problems, as required by OSHA and NIST.
-
Workplace Safety: Smart sensors and monitoring systems can spot dangerous situations right away. This helps prevent accidents, keeps workers safe, and makes the workplace safer overall.
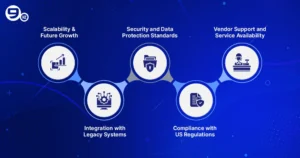
Factors to Consider Before Choosing IIoT Software
Scalability and Future Growth
Adoption of IIoT is a sustained investment rather than a one-time endeavor. Companies need to assess if the software can grow from managing a few dozen devices now to thousands in the future. Scalable, modular platforms facilitate expansion as production demands increase and avoid later, expensive migrations.
Integration with Legacy Systems
The majority of US industries continue to rely significantly on antiquated equipment and systems that are difficult to replace. This older infrastructure should be easily connected to by the appropriate IIoT platform without causing any operational disruptions. Modern IIoT tools and existing equipment can communicate easily thanks to compatibility features like OPC UA, Modbus, and REST APIs.
Security and Data Protection Standards
Cyberattacks on industrial systems are a major concern these days; therefore, security becomes a major aspect. Essential features for IIoT include encryption, intrusion detection, and role-based access. Customer trust and operational continuity can only be guaranteed with a secure platform; otherwise, sensitive production data can be at risk.
Compliance with US Regulations (NIST, ISA/IEC, etc.)
It’s really important to pick an IIoT platform that helps with compliance, since US industries have to follow a lot of strict rules. Compliance guarantees legal protection and prevents expensive disruptions in addition to efficiency.
-
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Offers an organized method for recognizing, safeguarding, detecting, reacting to, and recovering from cyberthreats. NIST-aligned IIoT platforms assist companies in improving risk management.
-
ISA/IEC 62443: ISA/IEC 62443 is a global rule that keeps industrial systems safe. It makes sure IIoT setups follow very strict safety and security rules. Cyber-physical threats are avoided, and vulnerabilities are decreased through compliance.
-
OSHA and EPA Guidelines: Strict oversight of worker safety and environmental impact is required by US occupational and environmental regulations. Automated reporting features on IIoT platforms make it simpler to stay in compliance and stay out of trouble.
Heavy fines, harm to one’s reputation, and the closure of operations can result from noncompliance with these standards. For this reason, when assessing any IIoT software, regulatory support is an absolute necessity.
Vendor Support and Service Availability
IIoT systems are intricate and need constant upkeep. Vendors with strong documentation, localized US teams, and round-the-clock support ought to be given preference.
Comparing Different Types of IIoT Software
Cloud-Based vs On-Premise IIoT Solutions
| Feature | Cloud-Based IIoT | On-Premise IIoT |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Quick and easy deployment since infrastructure is managed by the provider. Businesses needing a fast setup can go for this | Due to big on-site hardware, it requires a lot of time to setup |
| Cost | It reduces capital expenditure by ensuring subscription-based pricing. Besides, it has a lower upfront cost | Initial investment is very high because of servers, storage, and staff |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; can add devices and capacity quickly without major changes to infrastructure | Limited by physical infrastructure, scaling may require additional hardware and configuration |
| Data Control & Security | Data is stored in the cloud; security depends on vendor practices. Offers convenience but some compliance risk | Full control over data and security; ideal for sensitive operations where compliance is critical |
| Accessibility | Enables seamless remote operations from any location | Access is usually restricted to on-site or VPN-connected systems, limiting remote accessibility |
| Maintenance | Vendor handles software updates, patches, and general maintenance. Minimal in-house IT effort | The internal IT team is responsible for maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting |
Open-Source vs Proprietary Platforms
| Feature | Open-Source IIoT Platforms | Proprietary IIoT Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally free or low-cost, reducing upfront investment. Requires internal resources for setup and maintenance | High licensing and subscription fees. Costs include vendor support and software updates |
| Support | Relies on community support and internal IT teams. May lack guaranteed response times | The company gives full help, like training, fixing problems, and promises on how fast they will help (SLAs) |
| Security | Security depends on community updates and internal management; it may require extra effort to ensure compliance | Vendor-managed security with regular patches, audits, and compliance certifications |
| Innovation | Rapid innovation through community contributions and open collaboration | Innovation driven by vendor R&D; updates follow the vendor roadmap |
| Integration | Flexible integration with other open systems, but may require custom development | Easier integration with supported platforms; limited flexibility outside the vendor ecosystem |
Edge Computing and Hybrid IIoT Models
| Feature | Edge Computing | Hybrid IIoT Models |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The data is processed near the source, like sensors, machines, and gateways | For optimizing performance, it combines local edge processing and cloud-based analytics |
| Latency | Since data is analysed on-site, it gives extremely low latency that enables real-time decision making | Latency is moderate. The critical data gets processed at the edge. But the complex occurs in the cloud |
| Scalability | Minimal ongoing cloud fees | Balanced costs; local edge setup plus cloud subscriptions, but optimized for efficiency |
| Security | Strong security for sensitive data since it remains local and reduces exposure to external networks | Security is shared; critical data at the edge is protected, while cloud data relies on vendor security protocols |
| Maintenance | Requires on-site IT or technicians to maintain edge devices | Shared maintenance; cloud provider handles software updates while internal teams manage edge hardware |
Upfront vs Long-Term Costs
| Feature | Upfront Costs | Long-Term Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The one-time costs when you first buy and set up IIoT software | The regular costs while using the software, like maintenance, subscriptions, and upgrades |
| Examples | Stuff you need to buy and set up, like sensors, servers, software, installation, and training for employees | Ongoing costs like subscriptions, cloud hosting, updates, support, electricity, and replacing hardware |
| Budgeting | Requires significant initial capital investment; may affect short-term cash flow | More predictable and spread out over time; easier for operational budgeting, but can accumulate significantly |
| Impact on ROI | High upfront costs can delay initial ROI, but once deployed, benefits start accruing | Long-term costs affect net savings over the lifecycle; careful monitoring is needed to maximize ROI |
| Flexibility | Less flexible once invested; changes to infrastructure may require additional capital | More flexible; subscription-based or cloud services can scale with business needs |
Calculating ROI for US Manufacturers
Buying Industrial IoT software can save money and make work faster. Predictive analytics is like a warning; it tells you when machines might break before they happen. This way, you don’t have to spend extra on repairs, and machines last longer.
Real-time monitoring is also super helpful. It shows what’s slowing things down so problems can be fixed fast, and more work gets done with the same stuff. If machines don’t stop randomly, companies don’t lose money. Following rules from groups like OSHA, EPA, and NIST also keeps everything safe and avoids fines.
Even just using predictive maintenance can help companies make 20–30% more money in the first two years. That’s a big, real benefit.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Factors
When choosing an IIoT platform, it’s really important to understand something called Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). This isn’t just the price you pay at the start; it also includes things like training IT staff, hardware costs, subscription fees, and even the risk of downtime when software is updated.
There are some hidden costs too, like using more electricity or trying to make old machines work with new ones. A good company should explain all these costs clearly before you buy, so there are no surprises later.
By looking at both ROI (the money you gain) and TCO (the money you spend), US manufacturers can make smarter choices and get long-term value from IIoT, financially, operationally, and strategically.
Take a look…
20 Top IoT Development Companies (2025)
Emerging Trends in Industrial IoT Software (2025)
Role of AI and Machine Learning
IIoT is getting better because of AI and machine learning. They help plan work, find problems fast, and fix machines before they break. For example, Siemens uses AI in its factories to save money and stop machines from breaking.
By 2025, AI will be a big part of all top IIoT systems, helping companies work faster and make smart choices with data.
5G and Edge Computing Impact
Edge computing and 5G help computers work near the machines. This makes things faster and helps people make quick decisions. Bosch, for example, uses it in factories to check machine data nearby. It saves internet use and helps machines work better.
This also helps companies work faster, easier, and control big factories far away.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing Support
IIoT helps save energy and take care of the Earth. It can track carbon, make less waste, and watch how much energy is used. For example, GE uses IIoT in its factories to use less energy and produce less pollution.
These tools also help companies follow rules and make their factories kinder to the environment.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Case Study 1: General Electric – Predictive Maintenance Implementation
- Overview of the Company:
General Electric (GE) is a big company that works in energy, healthcare, and airplanes. In 2015, GE started using IoT in its factories to make its operations smarter. - Scenario:
In 2016, GE had big problems because its power machines stopped working unexpectedly. This made repairs more expensive and work slower. To fix this, GE added a system with IIoT sensors that watches the machines all the time and tells them if something might break. - Outcome:
Because of the new system, GE spent 20% less on repairs and had 30% fewer unexpected machine breakdowns. This helped their work run smoothly and made the machines last longer.
Lesson Learned:
- Data Integration: Accurate data collection and analysis depend on the IIoT sensors’ seamless integration with current machinery.
- Skilled Workforce: IIoT systems are more effective when employees are trained to decipher and act upon predictive insights.
- Scalability: By putting scalable IIoT solutions into place, facilities can grow gradually without experiencing operational disruptions.
Try IoT Software Now
Talk to our Experts
Request A Free Quote
Case Study 2: Siemens – Real-Time Monitoring for Energy Efficiency
- Overview of the Company:
Siemens is a major player in the global technology industry that specializes in automation, digitalization, and electrification. Siemens started a digital transformation journey in 2018 to use IIoT technologies to improve its manufacturing processes.
- Scenario:
In 2019, Siemens aimed to optimize energy consumption across its manufacturing plants to reduce costs and meet sustainability goals. To track trends in energy use and spot inefficiencies, the business implemented IIoT-based real-time monitoring systems.
- Result:
A 15% decrease in energy expenses and a notable drop in carbon emissions were caused by the actionable insights that the real-time monitoring system offered. Siemens’ dedication to sustainability was reinforced by the successful integration of these insights into its operations.
Lesson Learned:
- Continuous Monitoring: To quickly identify and address inefficiencies, data collection and analysis must be ongoing.
- Employee Engagement: Including staff members in energy-saving projects helps the company develop a sustainable culture.
- Technology Integration: Data accuracy and decision-making are improved by integrating IIoT systems with current energy management platforms.
Final Checklist for Choosing the Right IIoT Software
Questions to Ask Your Vendor
- How does your platform grow as your company does?
- Which legacy system integrations are supported?
- How do you make sure that US regulations are followed?
- What built-in security features are there?
- What is your SLA response time and support model?
Must-Have Features in 2025
- Predictive maintenance powered by AI
AI must be used by IIoT platforms to anticipate equipment failures before they happen. This guarantees optimal machine performance across all production lines, minimizes unscheduled downtime, and lowers maintenance costs. - Hybrid Compatibility of Edge and Cloud
A hybrid architecture uses cloud resources for advanced analytics while allowing critical data to be processed locally at the edge. This method enables scalable operations while lowering latency and bandwidth expenses. - Robust Encryption and Compliance with Cybersecurity
Strong security features are necessary to safeguard sensitive industrial data and preserve business continuity. These features include multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, and compliance with NIST/ISA/IEC standards. - Customizable analytics and real-time dashboards
Managers can keep an eye on performance, spot irregularities, and make data-driven decisions with interactive dashboards that provide real-time insights. Analytics that can be customized aid in coordinating the platform with particular operational objectives. - Tools for Monitoring Sustainability
In order to support green manufacturing initiatives, IIoT solutions should monitor waste, energy consumption, and carbon footprint. These resources support businesses in adhering to legal obligations while encouraging ecologically conscious practices.
Conclusion
By 2025, industrial IoT software will do more than just watch machines. It will also help check data in real time, save energy, fix machines before they break, and make factories more eco-friendly. Companies that start using it early can make smarter choices, waste less, and handle problems faster.
To start, companies should try small projects first to test sensors, connections, and data tools. Then they can slowly use it more. Training workers and connecting old machines with new ones helps a lot. Using cloud and edge computing with AI also makes things faster and safer.
In the end, IIoT is not just a new technology; it’s a way to work smarter. It helps companies save energy, work better, stay safe, and be ready for the future with smart machines and trained workers.
FAQs
Q1. What is the Industrial Internet of Things?
To increase productivity, safety, and efficiency in industrial settings, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) links machines, sensors, and other devices.
Q2. What is the difference between IoT and Industrial IoT?
While IIoT concentrates on industrial applications like manufacturing, logistics, and energy, IoT refers to consumer and commercial devices (such as smart homes).
Q3. What are Industrial IoT applications?
Predictive maintenance, smart manufacturing, supply chain tracking, energy optimization, and safety monitoring are some examples of applications.
Q4. What is the future of IIoT technology?
IIoT will be heavily dependent on edge computing, 5G, and AI by 2025, with a focus on sustainability and adherence to changing US regulations.
Great Together!