Factories are no longer a setting of manual labor operating machines; new era technology like IoT, AI, ML, and Industry 4.0 encompasses redefined intelligent production systems. Specifically, IoT, or Internet of Things, has been a game-changer tech for manufacturing that connects multiple sensors and devices into a unified platform. It deploys features such as real-time tracking, advanced analytics, and automated systems to enhance productivity and safety. The global market for IoT in manufacturing is forecasted to reach $45 million by 2029 to grow at a CAGR of 13%.
We can look at Bosch, which invested in smart factories to implement IoT across its global plants, resulting in a 25% increase in overall equipment efficiency. IoT-driven solutions in manufacturing are expanding, and existing dynamics will progress through the emerging trend of sensors and predictive maintenance. As an experienced IoT software development company, we explore how IoT in manufacturing works and how businesses can leverage these technologies to boost efficiency, which we cover in detail in this blog.
What is IoT in Manufacturing?
The IoT, or Internet of Things, in manufacturing refers to integrating the networks of multiple devices, sensors, software, and communication technologies to collect real-time data across the manufacturing process. IoT has enabled manufacturers to track real-time data for better decision-making to improve efficiencies and predict failures.
IoT in manufacturing directly implies using sensors, machines, and robots altogether for production lines while reducing downtime. Advanced solutions like 3D printing and intelligent systems can turn manufacturing faster, smarter, and more efficiently, following an agile production process.
Whether it’s tracking the movement of goods or offering predictive maintenance for equipment, IoT in manufacturing helps companies to gain a competitive advantage. Adopting the tech will help to reduce costs, shorten production time, offer more personalisation, and better safety controls.
Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
IoT has a huge demand in the manufacturing industry, as it can provide major benefits for operators, supervisors, and engineers to gain visibility into the production line. It helps businesses to make more data-centric decisions and optimise operations using IoT in manufacturing. Let’s explore a list of other benefits of integrating IoT in manufacturing:
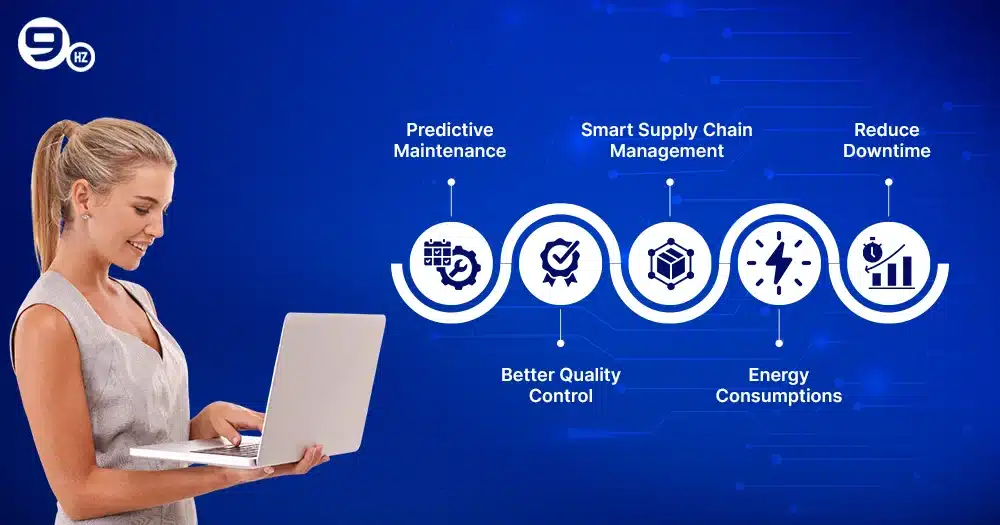
Predictive Maintenance
One of the key advantages of IoT in manufacturing is predictive maintenance that saves more investment and time for companies. The manufacturing sector is filled with breakdowns and system failures. IoT-based devices help to detect and send alerts to regularize operation and production lines. It allows for on-time repairs and maintenance that significantly reduces repair costs.
Better Quality Control
Quality assurance has been playing a central role in manufacturing, and IoT sensors ensure that each product is developed consistently. It continuously monitors multiple parameters like pressure, humidity, and temperature that can spot issues and send alerts for defects. IoT optimizes the quality control that does not halt production and improves efficiency.
Smart Supply Chain Management
IoT devices and sensors that help to track inventory, monitor for delivery routes, and predict stock levels. Building a smart system ensures that manufacturers’ raw materials or components will be available and there will be no shortage, causing no delays for production.
Energy Consumptions
Manufacturing involves a lot of energy consumption, and it is hard to manage costs during mass production. Using IoT sensors, manufacturers monitor for energy usage and target areas where energy is overutilised and automate adjustments. It helps to save major production costs to support achieving sustainability goals.
Reduce Downtime
Downtime has been a major disruptor in manufacturing, but with the help of IoT, it can significantly reduce the time lapse. IoT sensors can detect performance gaps for equipment and send an alert to technical experts so that they can address the challenge in advance and save resources and time.
Common Use Cases of IoT in Manufacturing
IoT (Internet of Things) creates value for collecting real-time data through sensors, and real-time data that provides manufacturers with the potential to optimise their production. One of the pioneers of transformative technology, IoT has varied use cases in the manufacturing sector. Let’s discuss some:
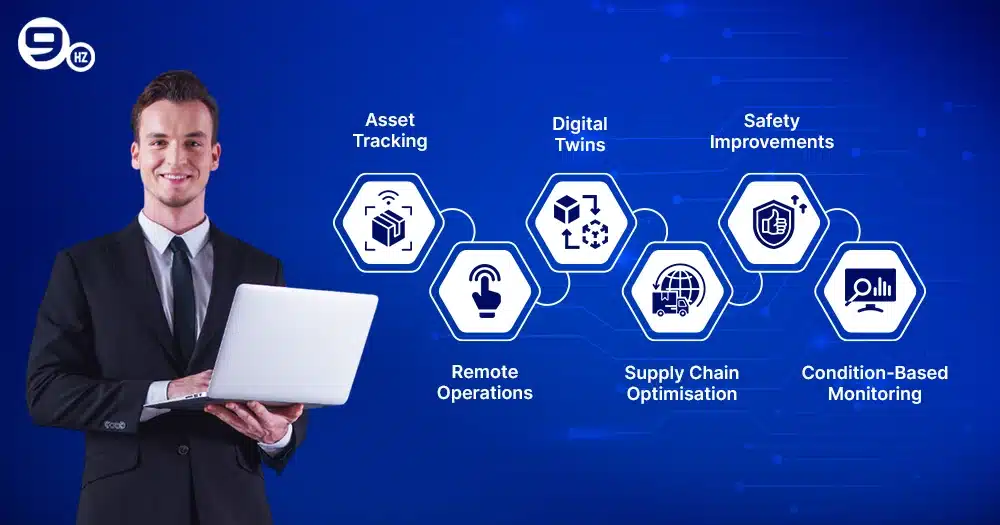
Asset Tracking
Manufacturers benefit from IoT-based asset tracking that takes less than a second to find equipment and optimise for usage. This helps prevent unauthorised asset use and theft to manage logistics and automate the sorting process. It provides a detailed analysis for manufacturing goods at different stages that eliminates blockers.
Popular brands like Caterpillar use IoT to track across different locations, as it can optimise logistics and supply chain operations.
Remote Operations
IoT devices are more compatible for remote processing and are configured to collect real-time updates for the production process. Remote access control can tune devices, saving you more time and effort to fix performance issues through virtual networks.
Bosch is developing IoT platforms to keep track of access control for equipment, to develop a centralised dashboard supporting remote operations.
Digital Twins
It is based on IoT technologies, where virtual copies of physical objects and their manufacturing applications are effectively monitored to reduce asset risk and damage. This helps engineers and managers to simulate the production process, conduct experiments, and achieve the desired results.
Unilevel is implementing digital twins for optimising production lines, which simulates the manufacturing process to test for quality changes.
Supply Chain Optimisation
Manufacturers are utilising IoT-based real-time inventory tracking to monitor demand forecasting and effectively manage their supply chain. It provides the right estimate for supply requirements to prevent a mismatch level during excess demand and avoid costly mistakes.
DHL integrates cloud analytics and IoT sensors for global analytics to support real-time visibility across the warehouse operations and last-minute delivery.
Safety Improvements
With the help of IoT sensors and automation, it is possible to improve safety measures and security for manufacturing. Also, it contributes to safeguarding conditions like noise levels, fatigue, or gas leaks through sensors and wearables. This enhances safety levels to monitor areas where hazardous conditions might appear.
Honeywell invests in developing connected wearable detectors and safety gear to alert industrial workers to detect dangerous levels across the oil and gas chemical plants.
Condition-Based Monitoring
One of the strongest maintenance strategies used in the manufacturing industry utilises real-time data to monitor equipment health. CBM monitors for early detections and tracks potential malfunctions to measure any deviations that occur when production exceeds normal operating conditions.
Tata Steel is implementing IoT-driven CBM to track compressors, monitor furnaces, and conveyor belts to detect early issues relating to unplanned stoppages, excess vibrations, and temperature spikes.
Challenges in IoT Implementation
Industry 4.0 has been leading the sector by introducing technologies like IoT that have become the forefront of value drivers to mitigate the risk for organisations. However, certain challenges exist for the real-world implementation of IoT in manufacturing:
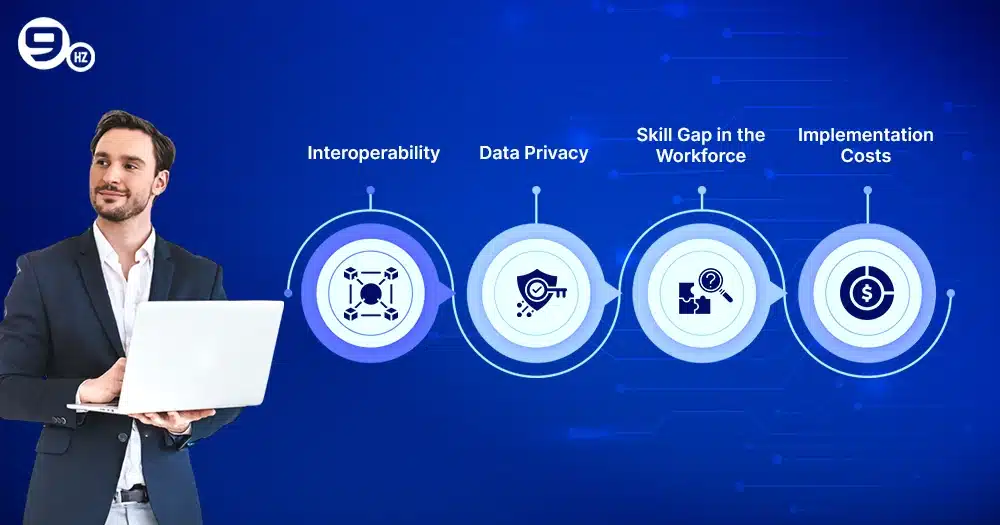
Interoperability
IoT devices integrating from different vendors might create interoperability challenges. This poses difficulty in finding a compatible tech stack that suits functionalities and requires adjustments. Devices come with multiple formats like XML, JSON, and other models; it is essential to follow standard data protocols and communication for improving interoperability.
Solutions: You can adopt a standard protocol like CoAP and MQTT that helps to integrate IoT devices and platforms. Also, integrating APIs allows for easy communication and data exchange through different systems.
Data Privacy
IoT integration helps to interconnect multiple devices that can easily transfer data for supply chain management, posing a challenge for data security. Companies might be at risk of cyberattacks, data privacy concerns for sensitive information.
Solutions: You can use authentic end-to-end encryption, secure authentication, and regular firmware and software updates. Also, adopting standards like NIST cybersecurity frameworks and ISO/IEC 27001 will help reduce privacy risks.
Skill Gap in the Workforce
For IoT implementation in manufacturing, it requires the right knowledge and skills related to hardware and software development, along with data security measures. The manufacturing team might take a longer time to learn about data analytics and IoT system management.
Solutions: Upskilling the workforce through IoT training programs, partnering with startups and educators to make them learn the technology, and hiring IoT consultants.
Implementation Costs
Another common challenge is for high IoT implementation cost investment to set up infrastructure, sensors, skilled labor, and others. Manufacturers are evaluating options that deliver the best ROI (Return on Investment) and long-term benefits, allowing for large-scale deployments.
Solutions: Businesses can start with a small-scale implementation to validate the technology that benefits overall use cases. Instead of development, they can collaborate with a partner for cost-effective IoT adoption.
Future Trends of IoT in Manufacturing
Combining technologies like IoT in innovative ways helps businesses to remain competitive within the industry. Emerging tech trends comprise industrial IoT, edge computing, 5G connectivity, smart factories, cybersecurity, and sustainability. Manufacturing businesses are looking for IoT trends for informed decision-making, integrating tools and data management. Here are the key trends for IoT in manufacturing:
AI-Based Predictive Maintenance
IoT sensors use automation to collect real-time data for early detection of any breakdowns and system failures. It enables predictive maintenance to fix operational issues and breakdowns through automated schedules. Manufacturers get the benefits of unexpected downtimes, maintenance schedules, and extended lifetime with production efficiencies.
Smart Factories
Rolling out 5G technologies revolutionising smart factories to establish smooth data transfer for IoT devices and systems across different locations. The manufacturing sector is setting up these to support real-time data sharing, remote operations, and integration for autonomous robots to support operational agility, precision, and flexibility.
Hyper-Personalisation
IoT as technology helps manufacturers to track customer preferences and demand variability to focus on customised production. Smart sensors, connected equipment, and data analytics adjust based on inputs like features, size, and production capacity. This trend allows for flexible manufacturing with minimal wastage and localised production.
Blockchain-Based Supply Chain Management
IoT sensors with Blockchain ensure end-to-end visibility and transparency for supply chain management. Following this trend allows businesses to build a smarter and secure system with data-backed accountability at every stage.
How to Get Started with IoT in Manufacturing?
IoT brings a major shift to the manufacturing industry, enabling real-time monitoring and automated quality checks. Now, once you understand that IoT has high potential, you must be confused about how to begin implementing IoT in manufacturing. So, here are the steps to be followed:
Step 1: Define Business Objective
You should begin by identifying problems to target, like downtime or product quality, which will help to find the ideal IoT strategy that aligns with business values, not just technology that grows more popular.
Step 2: Set up Tech Infrastructure
Next, you will be setting up tech-related infrastructure using network systems, equipment, and connectivity. So, identify the sensor’s capability and APIs to create the right integration with minimal disruptions.
Step 3: Start with Small Projects
You can pick any specific target, like asset tracking or maintenance, and implement it on a small scale to address long-run challenges. Also, use the pilot project to test for technology fit, ROI, and feasibility rather than implementing it across the whole plant.
Step 4: Selecting the Right Tool
Finding the right IoT platform that is compatible with data collection, device connectivity, real-time monitoring, and advanced analytics. Some of the popular tools include Siemens MindSphere, AWS IoT, and Microsoft Azure IoT.
Step 5: Install IoT Devices
At this stage, IoT implementation begins with deploying an IoT sensor for equipment and devices, with settings for measuring points like humidity, vibration, or temperature.
Step 6: Check for Network Security
For scalability and network stability, you can cross-verify for access control, encryption, and use secure protocols. Based on the factory location and machinery, you can use modular solutions that further allow for future expansions.
Conclusion
In the era of modern manufacturing, IoT solutions act as the backbone for automated production processes, enabling intelligent decision-making, real-time monitoring, and consistent machine-to-machine communication. Industrial robots connecting with IoT devices support easy data transfer and improve productivity while reducing unscheduled maintenance. More than 70% of supply chain managers are opting for technology solutions to increase operational efficiencies and automate repetitive tasks. So, businesses are analysing different use cases of IoT in manufacturing for quality improvements, reducing defective production, and enhancing safety through wearable tech for tracking hazardous behaviour.
Frequently Asked Question
What is IoT in the context of manufacturing?
IoT in manufacturing refers to interconnecting devices and sensors for collecting real-time data that helps with smarter decision-making and automation for production lines.
What are the top benefits of IoT in factories?
Some of the common benefits are increased productivity, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, supply chain visibility, and quality control.
How much does it cost to implement IoT in manufacturing?
The implementation cost will range between $10,000 to $5,00,000 based on device integration, devices, and scalability. It is advisable to use Cloud-based IoT and modular solutions that reduce upfront investment.
Can small manufacturers afford IoT adoption?
Yes, small manufacturers can start with low-cost IoT adoption and cloud platforms to adopt basic functionalities.
What industries benefit most from IoT-based manufacturing?
Some top industries are Food and Beverage, Aerospace, Automotive, Electronics, and Pharmaceuticals, which benefit from smart tracking, automated production, and real-time data updates.
Great Together!