Imagine you owned a mid-sized company before 2023, when AI agent use cases were unknown to many. There is a bulk of data, including inventory, market trends, and customer interactions, that your sales team needs to analyze to make real-time decisions. It is an overwhelming task and a costly affair that delays decision-making.
Fast forward to today, AI agents, i.e., autonomous systems that can act on your behalf, have it all automatically taken care of, from proactive data analysis and inventory management to offering customers personalized recommendations.
Automated repetitive tasks, such as data analysis, inventory management, and customer relationship management, are only a few examples of use cases for AI agents. The uses of AI agents pertain deep into many industries and enterprises of all sizes, leading to an exponential growth of AI-powered agents from $3.7 billion in 2023 to $150 billion in 2025.
Do you also wish to transform your business operations with Artificial Intelligence-based agents for real? or looking for an AI agent development company then, you are in the right place.
This article comprehensively answers all your questions, from helping you understand AI use cases by industry to teaching you how to build an AI agent.
Let us first understand AI agents, their working, and their types.
What Are AI Agents?
Autonomous agents created using AI technologies are applications that make decisions and perform business functions independently with minimum human intervention. Supported by advanced models, AI agents choose a course of action and execute it using multiple software tools.
While traditional software systems rely on predefined rules, AI agents work using new data and outcomes for better decision-making and can be of various types.
Partner With The NineHertz – Trusted Experts in AI Agent Development
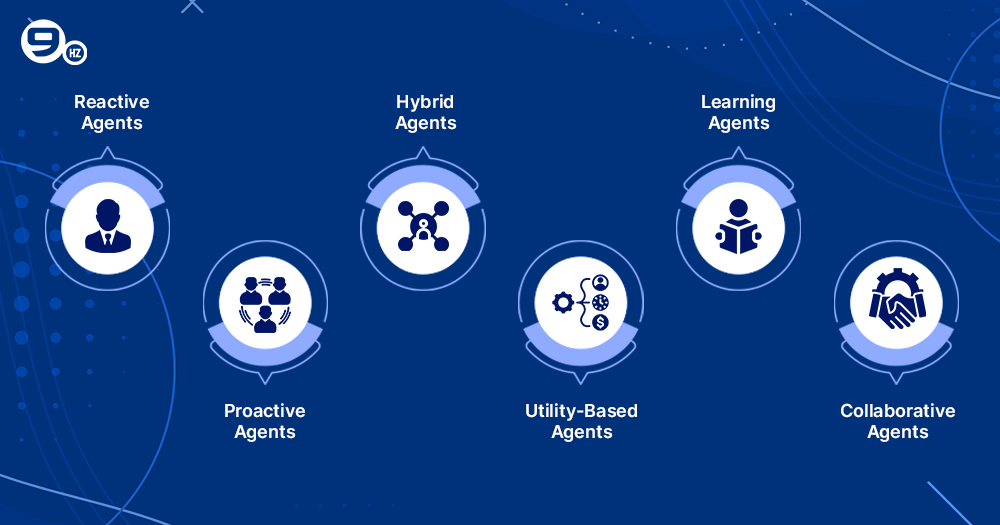
Types of AI Agents
Agents leveraging AI can be of different types, based on their complexity and decision-making process, such as follows.
1. Reactive agents
Also called reflex agents, Reactive AI agents are rule-based systems. These agents strictly follow user prompts and preset rules to function. While they are low-maintenance virtual assistants that need minimal programming, they do not have enough memory. Hence, the models based on Reflex agents are most suitable for short-term scenarios.
For example, suppose you wish to automate repetitive tasks, such as resetting the customer password using conversational phrases or keywords. In this scenario, you can deploy AI agents called chatbots to automate the process.
2. Proactive agents
Unlike simple Reflex agents, proactive AI agents apply predictive algorithms to execute more complex tasks. These models do not need human intervention or prompts to discern patterns, forecast possible outcomes, and select the most suitable course of action. Complex systems, such as supply chains, are some of these AI agents’ use cases.
PRO TIP: To make proactive AI agents effective, set up a clear feedback loop mechanism that allows the system to learn from its successes and failures. This continuous learning approach improves accuracy over time and helps avoid repeating mistakes.
For example, imagine you need help during peak seasons for demand forecasting. In this situation, you can deploy a proactive AI agent to forecast future demand using advanced algorithms to prepare for unexpected demand surges.
3. Hybrid agents
Hybrid AI models are a combination of reactive and proactive AI agents. Like simple reflex agents, they apply preset rules to automate repetitive tasks while using advanced predictive algorithms of proactive agents to respond to complex situations.
For example, consider a situation where you wish to automate routine tasks, such as the handling of customer inquiries. In this case, you can use a customer service chatbot based on a hybrid AI agent model. This agent first uses preset rules to handle repetitive or routine inquiries but applies advanced solutions (such as escalating complex issues to human agents) to solve complicated problems.
4. Utility-based agents
Imagine a robot in your office that completes all work and determines the optimal time and process, all without human help. That robot is a utility-based agent. These agents do not follow simple rules, rather, they weigh the pros and cons of all actions to choose the best option.
Another good example of Utility-based AI agents’ use cases can be seen in autonomous vehicles. The AI agents deployed in self-driving cars consider speed, safety, passenger comfort, fuel efficiency, and other factors when navigating roads. In this case, they may balance reaching the destination quickly against taking a longer but safer route, displaying their smart decision-making.
5. Learning agents
As the name suggests, Learning agents learn from their past experiences. They use machine learning techniques, such as unsupervised, supervised, or reinforcement learning, to improve performance. Unlike static AI systems, these agents continuously advance, learning from their actions and environment, adapting, and making better decisions using data and feedback.
PRO TIP: Set up a “sandbox” area for learning agents to practice and fail during training without interfering with core business operations. This enables more forceful learning approaches while keeping business risk to a minimum.
Have you used spam filters in your email? These spam filters are among the best examples of AI agents based on the learning model. They learn spam email identification based on your feedback and patterns in emails.
6. Collaborative agents
Collaborative AI agents, or multi-agent systems, coordinate their actions to accomplish complex goals. They create custom workflows, delegate tasks to other agents or people, and use one another’s expertise. It helps enhance problem-solving, improve efficiency, adapt to dynamic conditions, refine reasoning, and eliminate errors.
Let us explain with an example. Imagine a patient with complex symptoms arriving at a doctor’s clinic. It would be time-consuming for the doctor to analyze the complicated symptoms and diagnose the problem accurately. This is where collaborative AI agents’ use cases shine in healthcare management. An AI agent cross-references patients’ symptoms with medical databases, ensuring accurate diagnosis.
On that note, let us explore more AI use cases by industry to understand the scope of AI-powered agent solutions.
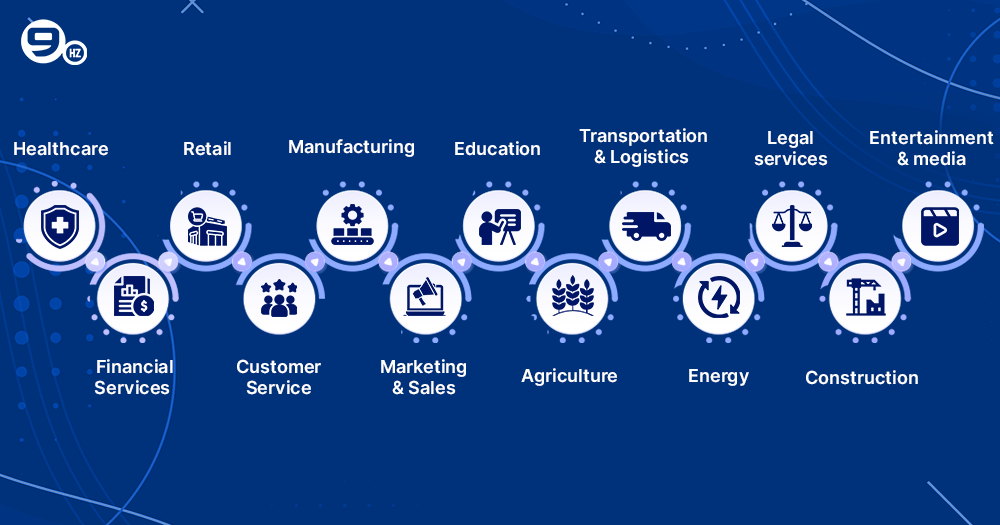
13 Industry-Specific AI Agent Use Cases
Here are some use cases for AI agents in various industries with examples and tools.
1. Healthcare
As seen through these examples, AI agents in healthcare transform medical research, patient management, and diagnostic accuracy.
Clinical decision support:
Combining patient information from multiple sources in clinical decision support systems helps doctors identify patterns through similar case comparisons and generate individualized treatment recommendations based on symptoms and past responses.
Patient care coordination:
Managing logistics and continued patient care are among the top AI agents’ use cases in healthcare. Patient care coordination agents handle logistics by using automatic systems to schedule appointments and monitor recovery progress against benchmarks while providing early intervention alerts and tracking medication adherence.
Medical research:
While medical research is a complex process, AI agents have transformed it. Potential compound identification, optimized clinical trials, treatment outcome prediction, and the following are some examples of AI agents’ use cases in biomedical research.
Moreover, medical research agents use their capabilities to process extensive research literature databases swiftly while developing hypotheses from diverse study patterns and selecting research directions according to their predicted impact and success rates.
Examples:
Providence Health Care uses coordination or multi-agent systems (MAS) from Memora Health to monitor patient recovery and manage their follow-up appointments.
2. Financial services
We can see more use cases for AI agents in the finance industry. Artificial Intelligence-powered agents go a long way in protecting people and financial institutions from fraud, as seen through these examples.
Detecting and preventing fraud:
AI agents have empowered financial institutions and their customers with better fraud detection and prevention. Real-time transaction monitoring through fraud detection and prevention systems uses behavioral pattern recognition to detect anomalies while taking immediate action through security alerts and transaction blocking for suspicious activities.
Algorithmic trading:
AI agents’ use cases are diverse in financial market trades. Continuously monitoring market conditions to identify patterns that may be profitable while making faster trading decisions than humans,processing multiple variables simultaneously for advanced strategies, and automatically adjusting trading positions when market conditions change are among the top examples of use cases for AI agents.
Personalized financial advisors:
AI agents’ use cases include tailored financial guidance. Personalized financial advisors create goals using goal-based agents with customized plans while building investment portfolios that match client risk profiles and targets, execute tax-efficient investment approaches, and deliver behavioral guidance during market turbulence.
Examples:
Mastercard uses Feedzai AI agents. These robotic process automation agents identify patterns and analyze them to detect potential fraud. It is among the best demonstrations of the use cases for AI agents in finance.
3. Customer service
Imagine identifying potential problems before your customers even spot them. Does that sound unbelievable? AI-powered agents have made it possible. Here is more about this and many other AI agents’ use cases in customer service.
Proactive customer support:
AI systems function ahead of customer requirements. The proactive customer support AI models follow customers’ past interactions to detect potential problems while making contact before issues worsen, handle customer lifecycle touchpoints, and identify patterns of potential customer churn to start retention strategies.
Call center augmentation:
Leveraging AI helps level up the customer support operations of human agents. The AI-powered solutions provide immediate access to real-time information and response suggestions to human representatives, identify customer emotions to select suitable responses, provide instant access to knowledge bases, generate automated interaction summaries, and analyze call patterns to determine training needs.
Intelligent chatbots:
One of the examples of AI agents’ use cases is efficiently handling customer queries. AI system-based intelligent chatbots use natural language processing to understand both formal and informal queries while maintaining context understanding for suitable responses, and they resolve standard issues like order tracking autonomously through customer history analysis to provide personalized support and transfer complex tasks to human agents with complete details.
Examples:
Zendesk uses Freshdesk’s virtual assistants based on AI technologies to address basic customer inquiries, offering proactive relationship maintenance and improving customer service.
4. Manufacturing
There are many use cases for AI in manufacturing industry. Let us look at some examples.
Predictive maintenance:
Intelligent agents detect equipment failures before they occur. The predictive maintenance systems use sensor data analysis to monitor equipment performance (from IoT sensors) while detecting small pattern changes.
Moreover, AI models determine when components will fail based on present conditions. These agents using artificial intelligence also help find recurring problem causes and schedule maintenance to reduce production stoppages.
Quality control:
Maintaining product standards is among the essential business functions of a manufacturing unit and the top AI agents’ use cases. Computer vision AI agents within quality control systems detect visual defects, acoustic analysis detects sound pattern deviations, and the system assesses multiple quality parameters simultaneously while providing real-time feedback for process adjustments and defect classification for targeted business process improvements.
Supply chain management and optimization:
AI systems go a long way in helping you manage and optimize production network operations. The core AI agents’ use cases in the supply chain include enabling complete visibility of materials and products while predicting disruptions through external factor analysis.
Moreover, you may deploy AI agents to optimize transportation routes and maintain distribution network inventory levels. Furthermore, Artificial intelligence agents also help evaluate supplier reliability to support procurement decisions.
Examples:
Global giant Unilever uses o9 Solutions to operate its complex international supply chains with increased resilience and efficiency.
5. Marketing and sales
AI agents work wonders in marketing and sales. Let us look at some examples of AI agents’ use cases to see how they help you market and sell better.
Lead scoring and qualification:
Your sales teams can prioritize prospects using AI agents. These systems analyze prospect interactions with marketing materials and correspondence through numerical value assignments to track engagement and predict conversion potential based on profiles and behaviors to help sales teams focus on high-potential prospects.
Content personalization:
AI systems can help you generate customized marketing materials. The possible AI agents’ use cases in content marketing include developing user preference profiles through past interaction analysis. It enables content selection for individual users while testing different content versions to determine top performers and maintain consistent personalized experiences across platforms.
Market research and analysis:
Researching and analyzing the target market is a crucial business function. Here is how AI agents can help you with it. The Market research and analysis AI systems track social media mentions of the brand, analyze user sentiment across discussions, detect emerging trends before they reach mainstream adoption, and monitor competitor activities to convert unstructured data into actionable business insights with generative AI.
Examples:
StoryChief boasts a built-in AI-powered marketing agent called William. It performs keyword research, language translation, traffic monitoring, and content calendar optimization for online marketing, perfectly demonstrating the AI agents’ use cases.
6. Education
AI agents in education customize learning experiences, automate routine tasks, and enable continuous assessment for improved results. Here is more on the AI agents’ use cases in the education industry.
Adaptive learning:
The adaptive learning AI platforms analyze student learning patterns to create personalized educational content. Moreover, they automatically adjust difficulty levels based on performance, identify knowledge gaps for targeted intervention, and suggest specific resources for struggling students.
Automated administrative tasks:
The administrative system automates course scheduling, enrollment processes, resource allocation, and attendance tracking. Moreover, AI-powered agents send automated notifications to students and parents regarding deadlines, academic progress, and assignments.
Learning analytics:
Learning analytics uses tracking technology to monitor student material engagement through behavioral pattern analysis to predict academic success, detect students needing early dropout prevention, and assess teaching method effectiveness.
Examples:
The University of Arizona uses Civitas Learning’s predictive AI data analytics to improve student retention rates by 5-10%.
7. Agriculture
There are diverse AI agents’ use cases in agriculture. Artificial intelligence helps optimize resource allocation, crop management, and monitor livestock. Here is more on it.
Precision farming:
The precision farming AI systems analyze crop health through satellite imagery and drone data to create optimized irrigation and fertilization schedules based on soil conditions and detect early disease or pest infestations while generating yield predictions for better harvest planning.
Resource management:
The resource management AI agent systems track water consumption to create optimized irrigation plans through weather data and crop requirement analysis, select suitable seeds for different soils, control farm energy usage, and schedule equipment maintenance.
Monitoring livestock:
The AI system tracks animal health metrics from individual livestock through wearable sensors, uses behavior analysis to detect illness early, optimizes feeding schedules according to nutritional requirements, and monitors reproductive cycles for better breeding results.
Examples:
Land O’Lakes uses the R7 Tool from WinField United to maximize fertilizer efficiency, which reduces expenses while delivering better environmental results.
8. Transportation and Logistics
Examples of AI agent use cases in transport and logistics include route optimization, fleet management, and improved delivery operations. Below is more about these use cases.
Route optimization:
The system uses route optimization to analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions, and delivery priorities for determining optimal routes and makes real-time delivery schedule adjustments based on changing conditions and coordinates multiple pickup and delivery sequences, and distributes workload evenly among delivery fleets.
Fleet management:
Intelligent agent systems track vehicle performance data to forecast maintenance requirements, optimize vehicle assignments according to cargo needs and driver status, evaluate driver conduct for safety enhancement purposes, and control fuel usage by optimizing routes and driving patterns.
Enhanced delivery operations:
The AI-powered agent system provides precise delivery window predictions, consolidates packages for efficient delivery, manages autonomous vehicle and drone operations, and delivers real-time updates to recipients.
Examples:
UPSimplemented ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation). It saved more than 100 million miles while decreasing fuel usage by 10 million gallons.
9. Energy
AI agents in energy management optimize production and distribution and enhance maintenance capabilities for traditional and renewable energy systems. Here are a few examples of AI agents’ use cases in the energy sector.
Grid management:
AI-powered agents manage power distribution through real-time balancing of supply and demand while predicting consumption to optimize distribution, integrating renewable sources, and detecting grid anomalies to stop outages.
Optimized renewable energy:
The AI-based optimization system for renewable energy uses weather forecasts to predict solar and wind production while it manages battery storage operations and microgrid stability and facilitates energy trades between producers and consumers.
Predictive maintenance:
The AI agent system tracks equipment performance in power generation, forecasts equipment failures, maintains optimal maintenance schedules to reduce downtime, and lengthens equipment life by taking proactive measures.
Examples:
General Electric enables utilities to achieve a 30% reduction in outages through their Digital Energy Grid Analytics platform, enhancing asset utilization.
10. Legal services
AI agents in legal services enable document review streamlining while improving research abilities and case management to boost operational efficiency. Here are their use cases.
Document analysis:
The AI-powered document analysis system examines legal documents and contracts to reveal essential clauses and possible risks. It also checks documents against standard templates, pulls important data from lengthy documents, and detects inconsistencies between related documents.
Legal research:
AI agents examine legal precedents and case laws to find applicable decisions and use historical data for outcome predictions. Moreover, generative AI creates detailed research summaries and helps detect regulatory noncompliance.
Case management:
AI-powered solutions use urgency and complexity to determine case priorities. Moreover, these agents distribute resources to different matters, monitor deadlines and statutes of limitations, and identify patterns in similar cases to generate strategic insights.
Examples:
JP Morgan uses the COIN (Contract Intelligence) system to analyze commercial loan agreements in seconds, saving an estimated 360,000 hours of lawyer time.
11. Construction
Do you find project planning, safety monitoring, and resource management challenging in the construction industry? Then here is how autonomous agents can help you with these complex tasks.
Project planning:
Project-planning AI agents predict construction timelines through historical data analysis and assessing current conditions. Moreover, these systems optimize resource distribution between project phases, generate construction sequence simulations to find efficient methods, and evaluate design modification effects.
Safety monitoring:
The AI system employs computer vision technology to detect safety infractions at construction sites, uses site conditions to forecast dangers, assesses worker fatigue and stress levels, and enforces safety standards.
Resource management:
The responsible AI systems track material consumption, forecast upcoming needs, deploy equipment between sites efficiently, schedule subcontractors better, and assess energy usage for sustainability goals.
Examples:
Suffolk Construction uses AI-powered cameras from Smartvid.io to detect safety risks. These cameras helped reduce recordable incidents by 30%.
12. Entertainment and media
Personalized content recommendations, production process optimization, and enhanced audience engagement are the top examples of AI agents’ use cases in entertainment and media. Let us learn more about them.
Content recommendation:
AI technologies analyze data such as viewing and listening habits to suggest relevant entertainment, predict new content trends, personalize promotional materials, and optimize content discovery interfaces.
Production optimization:
AI agents analyze historical performance data to judge script effectiveness and predict audience reception. Moreover, these systems optimize shooting schedules, allocate resources, and automate post-production tasks (for example, initial editing and color correction).
Audience analytics:
Intelligent agents divide viewers into segments through engagement pattern analysis, predict demographic-specific content performance, determine optimal release times for maximum reach, and assess cross-platform content performance.
Examples:
Warner Bros. uses Cinelytic AI tools to forecast box office success, leading to better release planning and increasing their return on investment by 15-20%.
13. Retail
There are many examples of use cases of AI agents in the retail industry. Here are a few of them.
Inventory management:
Agent technologies help manage inventory by optimizing product availability. The inventory management system uses historical sales data and market trend analysis to predict upcoming demand requirements.
Moreover, artificial intelligence systems analyze inventory levels between locations to achieve maximum sales through reduced excess stock. Furthermore, autonomous agents conduct automatic reordering at beneficial times, detect discount opportunities for slow-moving products, and suggest product assortments by location.
Customized retail interactions:
Let us understand AI agents’ use cases in customizing shopping experiences. The generative AI system generates personalized retail recommendations through historical data analysis and customer pattern recognition.
Moreover, it customizes website content to create individualized promotion offers, suggests related products for cross-selling, and groups customers with similar tastes for better personalization.
Virtual assistants in shopping:
AI agents’ use cases examples include how virtual shopping assistants apply natural language processing to understand customer queries while providing product database navigation.
Moreover, AI technology-based image-based search functionality, try-before-you-buy experiences, and essential product specifications and comparisons are other crucial use cases for AI agents.
Examples:
Amazon uses Dynamic Yield AI-powered agents as recommendation agents to generate substantial sales through customized suggestions. It is among the best examples of how you may deploy AI agents in retail.
These AI agents’ use cases demonstrate how AI agents help you ensure efficient business operations and capabilities beyond traditional technologies. Let us walk you through more of its benefits.
6 Benefits of Using AI Agents
Along with minimizing human intervention, Artificial intelligence agents have many benefits, such as the following.
- Round-the-clock availability: Human agents need breaks to function, while AI agents provide continuous operation. It ensures uninterrupted service availability.
- Scalability: AI systems maintain their operational capacity through fluctuating workloads without needing extra staff expenses. Hence, it is suitable for your business if you have variable customer demand.
- Data-based decisions: AI agents analyze extensive data sets to identify patterns that human analysis might overlook.
- Long-term cost savings: Robotic process automation reduces substantial operation costs, even if you need to make initial investments.
- Customized experiences: You may deploy AI agents to deliver personalized experiences to customer bases that extend into thousands or millions.
- High accuracy: AI systems perform complex tasks with precise accuracy, minimizing human mistakes during essential operational processes.
Let us share a real-world case study that perfectly demonstrates AI agents’ use cases and benefits.
AI Agent Useful Case Study: Anthem Health Insurance (Elevance Health)
The AI agent deployed by Anthem (now Elevance Health) throughout their customer service operations delivered outstanding results. Sydney, the virtual assistant, processes more than 60% of customer inquiries autonomously.
Challenge
Anthem received many calls daily, while they wanted to enhance customer satisfaction and reduce operational expenses.
Solution
The organization built an AI agent system that performed the following functions:
- The AI system processed natural language inquiries, operating through various communication channels.
- Sydney, an AI-powered agent, securely accessed customer records.
- Anthem’s AI system provided human agents with complete context when transferring complex cases between operators.
Results
- Sydney’s implementation resulted in a 47% decrease in operational costs for customer service.
- Anthem achieved a 26% higher score in customer satisfaction measurements.
- After AI agent deployment, Anthem’s response time decreased by 83%.
- AI systems increased the first-contact resolution rates by 38%.
Successful AI agent implementation motivated Anthem to deploy AI agents for other operations, such as provider network management and care coordination.
6 Challenges and Limitations in AI Agent Implementation
Despite multiple AI agents’ use cases and potential advantages, AI systems have many challenges. Let us understand a few Challenges you may experience when implementing them.
- Compromised privacy and security: AI agents access sensitive data, raising privacy and security concerns.
- Complex implementation: The process of integrating AI agents into current systems may be both complex and resource-consuming.
- Resistance from employees and customers: The acceptance of autonomous systems may face resistance from customers and employees. They may hesitate to use AI-powered agents for crucial decisions and services.
- Difficulties handling complex situations: AI agents experience challenges when handling complicated scenarios that need human emotional understanding and decision-making abilities.
- Ethical concerns: Autonomous systems generate ethical questions about responsibility, transparency, and potential bias in decision-making processes.
- Technical issues: The reliance on AI systems creates vulnerabilities because these systems may experience technical problems or system failures.
PRO TIP: Set up an “AI ethics committee” with diverse representation from various departments and backgrounds. The committee should review AI agent implementations for potential bias, privacy concerns, and ethical implications before deployment and periodically thereafter. This proactive governance approach helps identify and address issues before they become problems.
How to Get Started with AI Agents?
Successfully integrating AI agents into your organization isn’t just about the tech—it’s about aligning strategy, infrastructure, and people. Here’s a streamlined roadmap to guide your journey:
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Opportunities
Start by evaluating your core business processes. Look for repetitive tasks, decision-heavy workflows, or areas where delays cost time and revenue. These are ideal candidates for AI agent integration.
Step 2: Launch a Focused Pilot Project
Begin with a targeted pilot—think small, but strategic. Whether it’s automating lead qualification in sales or improving ticket resolution in support, a pilot helps you demonstrate ROI without the risk of full-scale rollout.
Step 3: Choose Between Building or Buying
Your organization needs to decide between building your own AI agents from scratch or utilizing existing platforms and solutions. This decision depends on your timeline, technical expertise, and need for customization. We help you assess the right fit based on your business goals.
Step 4: Hire a Professional AI Development Partner
If you’re unsure where to begin—or simply want to accelerate your progress—bringing in an experienced AI development partner can be a game-changer. A seasoned team brings proven frameworks, technical skills, and strategic clarity to ensure your AI agent deployment is successful from day one.
Step 5: Assess Your Data Infrastructure
AI agents thrive on high-quality data. Evaluate whether your organization has the right volume, structure, and accessibility of data to support intelligent automation. If not, we can help set up the foundations.
Step 6: Design Human-AI Collaboration
The goal isn’t to replace employees, it’s to empower them. Design workflows where AI agents assist, recommend, and enhance, while humans focus on creative and strategic decision-making.
Step 7: Implement Continuous Monitoring
AI agents aren’t fire-and-forget. A continuous monitoring system and feedback mechanism should be implemented to evaluate and improve the AI agent’s performance.
Step 8: Prepare for Change Management
Integrating AI isn’t just technical—it’s cultural. Communicate openly, train teams, and build trust around the use of AI agents in daily operations. This ensures long-term success and user adoption.
Looking at these steps, does building AI agents seem more like a hassle than a convenience? Then, here is The NineHertz at your rescue. Let us look at what we can do for you.
Looking at these steps, does building AI agents seem more like a hassle than a convenience? Then, here is The NineHertz at your rescue. Let us look at what we can do for you.
How Can The NineHertz Help You Build Custom AI Agents?
The NineHertz operates as a leading AI development company that develops business-specific AI solutions to solve various organizational problems. Our team specializes in healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and many other industries to deliver customized solutions for your unique business needs. We implement industry best practices, and our comprehensive approach includes the following.
- Strategic consultation: Our team helps you select the most important AI agent applications to benefit your business operations and market environment.
- Tailored development: AI engineers and data scientists at The NineHertz construct specialized agent solutions that meet the distinct needs of your organization.
- Effortless integration: Our team ensures your new AI agents integrate perfectly with all your current systems and operational workflows.
- Comprehensive training and support: We deliver complete training for your team members and continuous technical support for all AI systems.
- Continuous development: Our method involves continuous improvement, allowing your AI agents to grow with your business requirements and technological advancements.
Final Thoughts
AI agents are the future direction for business automation and intelligence. Organizations with strategic AI agent deployment will substantially benefit from these technologies. These agents will enhance efficiency and deliver better customer experiences and data-based decision-making capabilities.
Organizations should implement thoughtful success strategies by defining clear objectives, selecting appropriate AI agents’ use cases, and designing systems that leverage AI agent capabilities alongside human strengths.
An active approach to potential challenges and working with experienced technology partners can help businesses from all industries unlock AI agent transformation. Future success will belong to organizations treating AI agents as strategic assets to create new business models and capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Difference Between AI and AI Agents?
AI refers to the broader concept of machines simulating human intelligence, while AI agents are specific autonomous systems designed to perceive environments, make decisions, and act to achieve goals with minimum human intervention.
2. How Much Does it Cost to Build an AI Agent?
The cost of building an AI agent varies based on complexity. It typically ranges from $50,000 for basic implementations to $500,000 for sophisticated enterprise solutions.
3. Can Small Businesses Benefit from AI Agents?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from various affordable AI agent solutions that address their specific needs in customer service and scheduling their marketing automation.
4. How Long Does it Take to Implement an AI Agent Solution?
The implementation duration for basic applications spans 3 to 6 months, while enterprise-wide complex systems are completed in 12 to 18 months.
5. Do AI Agents Require Ongoing Maintenance?
AI agents need continuous monitoring and updates to ensure they perform well while adapting to new conditions and technological advancements.
Great Together!